Efficiency of biological products in the coinoculation of soybean
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.52755/sas.v2i2.109Keywords:
Biological fixation, glycine max, productivity, protectionAbstract
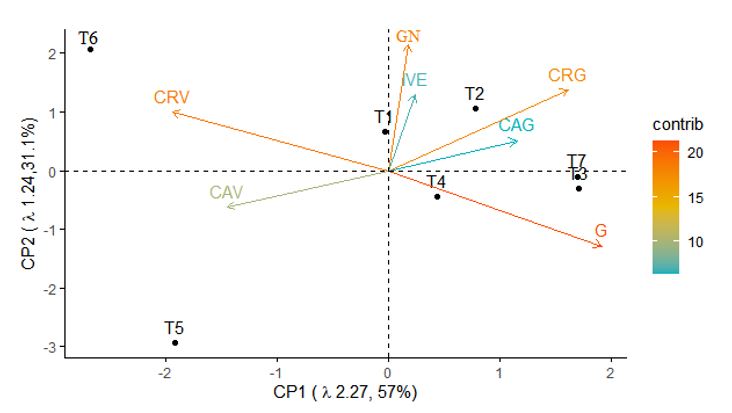
The objective of this work was to verify the potential use of comercial biological products in coinoculation with Bradyrhizobium japonicum in the treatment of soybean seed. Seven treatments were carried out with five repetitions, being: T1 – Control, T2 – Only Bradyrhizobium japonicum, T3 – B. japonicum + Azospirillum brasilense, T4 – B. japonicum + Bacillus subtilis, T5 – B. japonicum + Bacillus amyloliquefaciens, T6 – B. japonicum + Bacillus methylotrophicus e T7 – B. japonicum + Bacillus pumilus. The analyzed variables were germination (G),
germination of normal seedlings (GN), emergence speed index (IVE), and, at the end of eight days, aerial part growth in pot (CAV) and germitest paper (CAG), potted root (CRV) and germitest paper (CRG). The data were subjected to analysis of the assumptions and determined from the Tukey test at 5% probability and the principal component analysis (ACP). It was possible to observe that the coinoculation of B. japonicum + A. brasilense promoted rooting and germination gains in soybean seedlings. Coinoculation with B. pumilus showed an effect potential similar to the association of B. japonicum + A. brasilense. The association with B. methylotrophicus showed better rooting in pot (CRV) than the other treatments. The use of BPCP"™s in association with B. japonicum enhances the initial development of the plant.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2021 Luana Patrícia Pinto Korber, Ângelo Henrique Canan Korber, Luciana Grange, Celestina Alflen Klahold

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Autores concordam com os seguintes termos:
a) Os autores mantêm os direitos autorais e concedem à revista o direito de primeira publicação, com o trabalho simultaneamente licenciado sob a LicençaAttribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International, que permite o compartilhamento do trabalho com reconhecimento da autoria e publicação inicial na Revista SAS. A licença permite o uso, a distribuição e a reprodução irrestrita, em qualquer meio, desde que devidamente citada a fonte. Essa licença permite também que outros remixem, adaptem e criem a partir do seu trabalho para fins não comerciais, desde que atribuam a você o devido crédito e que licenciem as novas criações sob termos idênticos.
b) Não cabe aos autores compensação financeira a qualquer título, por artigos ou resenhas publicados na South American Sciences.
c) Os conceitos expressos nos artigos publicados na South American Sciences são de inteira responsabilidade de seus autores.








