Effect of pequi fruit (Caryocar brasiliense) on body composition and blood pressure of physically active adults: a quasi-experimental study
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.52755/sas.v2i2.156Palavras-chave:
Pequi oil, Physical exercise, Body composition, Blood pressureResumo
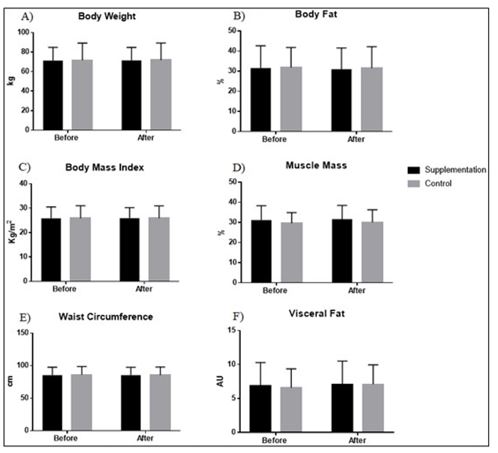
Physical exercise is known to promote several health benefits. Pequi is a very known fruit in the central region of South America. It is argued that pequi oil supplementation may enhance physical exercise adaptations, such as body composition and blood pressure improvement. However, few studies are available on this topic, and they are not conclusive. Purpose: to investigate the effect of pequi oil supplementation combined with physical exercise on body composition and blood pressure of healthy subjects. Methods:Â Twenty-three subjects (n=13 women, 30.2 ± 5.7 years, 1.66 ± .09 m, 71.5 ± 15.4 Kg) were allocated in two groups: exercise with supplementation (ExeS, n=11) and exercise without supplementation (Exe, n=12). ExeS and Exe performed at least two exercise sessions per week for a period of thirty days. Also, ExeS was supplemented with 400mg/day of pequi oil capsules. Body composition and blood pressure were analyzed before and after the intervention. Differences between groups were assessed by repeated measures analysis of variance adopting P < .05. Results: Body fat percentage did not differ (P > .05) between ExeS and Exe, respectively, before (31.5 ± 11.0 % vs 31.9 ± 9.9 %) and after (30.9 ± 10.5 % vs 31.5 ± 10.6 %) the intervention. Muscle mass and blood pressure also did not present significant changes (P > .05) intra and between groups in both moments. Conclusion: Pequi oil supplementation (400mg/day) for thirty days does not influence body composition and blood pressure of healthy and physically active subjects.
Downloads
Downloads
Publicado
Como Citar
Edição
Seção
Licença
Copyright (c) 2021 Pedro Ferreira Alves Oliveira, Mariana Soares Pereira, Lucas Amaral Pereira, Mateus Medeiros Leite, Maurílio Tiradentes Dutra

Este trabalho está licenciado sob uma licença Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Autores concordam com os seguintes termos:
a) Os autores mantêm os direitos autorais e concedem à revista o direito de primeira publicação, com o trabalho simultaneamente licenciado sob a LicençaAttribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International, que permite o compartilhamento do trabalho com reconhecimento da autoria e publicação inicial na Revista SAS. A licença permite o uso, a distribuição e a reprodução irrestrita, em qualquer meio, desde que devidamente citada a fonte. Essa licença permite também que outros remixem, adaptem e criem a partir do seu trabalho para fins não comerciais, desde que atribuam a você o devido crédito e que licenciem as novas criações sob termos idênticos.
b) Não cabe aos autores compensação financeira a qualquer título, por artigos ou resenhas publicados na South American Sciences.
c) Os conceitos expressos nos artigos publicados na South American Sciences são de inteira responsabilidade de seus autores.








